reading-notes
Code 201 Reading Notes
Process and Design (Chapter 18)
Before creating any webiste, we gotta know why we are creating it and for whom. We need to understand our audience to target them with the website.
Two types to target your audience with WHAT QUEASTION
| individual | Company |
|---|---|
| What is the age range of your target audience? | What is the size of the company or relevant department? |
| Will your site appeal to more women or men? What is the mix? | What is the position of people in the company who visit your site? |
| What is the average income of visitors? | Will visitors be using the site for themselves or for someone else? |
| What kind of device do they use to access the web? | How large is the budget they control? |
Why People are visitign your website ?
Your content and design should be influenced by the goals of your users. Also, People are visiting any website that meet their goals and desires. for example: A guy who is looking for a food to order, will not visit any website that does not belong to foods.
Your content and design should be influenced by the goals of your users
First you want to create a list of reasons why people would be coming to your site. You can then assign the list of tasks to the fictional visitors you created in the step described on the previous page.
What Information Your Visitors Need
You may want to offer additional supporting information that you think they might find helpful.Look at each of the reasons why people will be visiting your site and determine what they need to achieve their goals
How Often People Will Visit Your Site
Once a site has been built, it can take a lot of time and resources to update it frequently.Working out how often people are likely to revisit your site gives you an indication for how often you should update the site.
1. Site Maps
The aim is to create a diagram of the pages that will be used to structure the site. This is known as a site map and it will show how those pages can be grouped.
2. WireFrames
A wireframe is a simple sketch of the key information that needs to go on each page of a site. It shows the hierarchy of the information and how much space it might require.
3. Getting your message across using design
The primary aim of any kind of visual design is to communicate. Organizing and prioritizing information on a page helps users understand its importance and what order to read it in.
4. Visual hierarchy
Most web users do not read entire pages. Rather, they skim to find information. You can use contrast to create a visual hierarchy that gets across your key message and helps users find what they are looking for.
4. grouping and Similarity
When making sense of a design, we tend to organize visual elements into groups. Grouping related pieces of information together can make a design easier to comprehend. Here are some ways this can be achieved.
5. Designing Navigation
Site navigation not only helps people find where they want to go, but also helps them understand what your site is about and how it is organized. Good navigation tends to follow these principles…
What is ABC
1st | 2nd — | — A | What is a script and how do I create one ? B | How do computers fit in with the world around them? C | How do I write a script for a special webpage ?
A
A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow to achieve a goal.
B
COMPUTERS CREATE MODELS OF THE WORLD USING DATA
C
By using the HTML, CSS, & JAVASCRIPT
HTML & CSS
Structure
What is Structure
Structure is structure is very important in helping readers to understand the messages you are trying to convey and to navigate around the document, so in order to learn how to write a webpage, we need to understand how to strcuture document, it is very important

How Pages Work
Pages has different type of structure to be written, but most of it has the sme in common. Web pages or paper pages are sharing the same structure when it comes to work, where you can see images, headlines, subheadings and etc, but for the webpage you can add more like Audio or GIF or even some videos to clear the idea. sa
Structuring Word Documents
In word Documents, we can use large heading followed by an importants notes and information can help the reader to understand more. we can devide our topics to parahraph or we can make different headings to describe what it covers
HTML Describes the Structure of Pages
When it comes to webpages, we use some codes in order to interact, design and add text to have the latest output.
HTML Uses Elements to Describe the Structure of Pages
- Codes
- Tags
- Attributes
- Body Head and Tittle
Creating a webpage on PC/Windows
To start Create a webpage on PC, follow these steps
- Click Start > Prpgrams > accessories > Notepad or Right Click with your mouse > New > Notepad.
- write the code as in the picture below

3.Save as the file as first-test-html.
- Start your web browser. Go to the File menu and select Open. Browse to the file that you just created, select it and click on the Open button. The result should look something like the screen shot below.
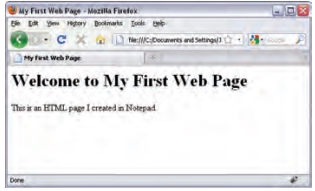
-
Yalaaa, your first webpage. Congrats
Extra Markup (Chapter 8)
The Evolution of HTML
Each new version was designed to be an improvement on the last (with new elements and attributes added and older code (removed)
-
HTML 4 With the exception of a few elements added in HTML5 , the elements you have seen in this book were all available in HTML 4.
-
XHTML 1.0 In 1998, a language called XML was published. Its purpose was to allow people to write new markup languages. Since HTML was the most widely used markup language around, it was decided that HTML 4 should be reformulated to follow the rules of XML and it was renamed XHTML. This meant that authors had to follow some new, more strict rules about writing markup. For example:
- Every element needed a closing tag (except for empty elements such as
).
- Attribute names had to be in lowercase.
- All attributes required a value,and all values were to be placed in double quotes.
- Deprecated elements should no longer be used.
- Every element that was opened inside another element should be closed inside that same element.
- HTML5
In HTML5, web page authors do not need to close all tags, and new elements and attributes will be introduced
DOCTYPE
Because there have been several versions of HTML, each web page should begin with a DOCTYPE declaration to tell a browser which version of HTML the page is using (although browsers usually display the page even if it is not included). We will therefore be including one in each example for the rest of the book
Comments in HTML
If you want to add a comment to your code that will not be visible in the user’s browser, you can add the text between these characters:
ID Attribute
Every HTML element can carry the id attribute. It is used to uniquely identify that element from other elements on the page. Its value should start with a letter or an underscore (not a number or any other character).It is important that no two elements on the same page have the same value for their idattributes
Class Attribute
Every HTML element can also carry a class attribute. Sometimes, rather than uniquely identifying one element within a document, you will want a way to identify several elements as being different from the other elements on the page.
Block Elements
Some elements will always appear to start on a new line in the browser window. These are known as block level elements.
HTML5 Layout (Chapter 17)
HTML5 is introducing a new set of elements that help define the structure of a page.
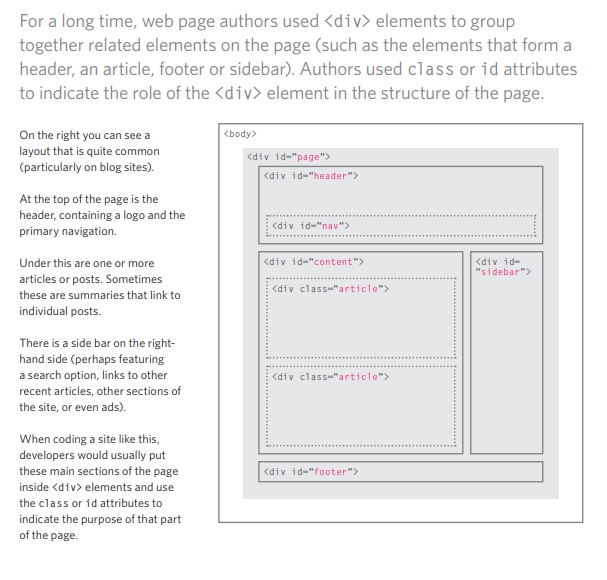
Traditional HTML Layouts
to have more information about Traditional HTML Layouts, See the image below
New Html5 LayoutElements
to have more information about Traditional HTML Layouts, See the image below
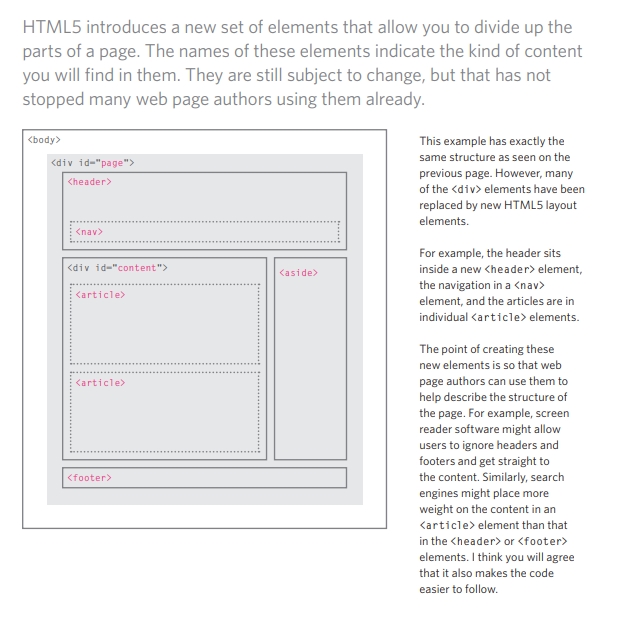
Headers & Footers
The <header> and <footer>elements can be used for:
- The main header or footer that appears at the top or bottom of every page on the site.
- A header or footer for an individual <article> or <section> within the page.
Navigation
The <nav> element is used to contain the major navigational blocks on the site such as the primary site navigation.
Articles
The <article> element acts as a container for any section of a page that could stand alone and potentially be syndicated.
Sections
The <section> element groups related content together, and typically each section would have its own heading
Heading Groups
The purpose of the <hgroup>element is to group together a set of one or more <h1> through <h6> elements so that they are treated as one single heading
Figures
You already met the
Sectioning Elements
It may seem strange to follow these new elements by revisiting the <div> element again. (After all, the new elements are often going to be used in its place.) However, the <div> element will remain an important way to group together related elements because you should not be using these new elements that you have just met for purposes other than those explicitly stated.
Linking Around Block-Level Elements
HTML5 allows web page authors to place an element around a block level element that contains child elements. This allows you to turn an entire block into a link.This is not a new element in HTML5, but it was not seen as a correct usage of the element in earlier versions of HTML.
Helping Older Browsers Understand
Older browsers that do not know the new HTML5 elements will automatically treat them as inline elements. Therefore, to help older browsers, you should include the line of CSS on the left which states which new elements should be rendered as block-level elements.