reading-notes
Text
There are two types to add a markup to the text:
1- Structural markup
To describe both headings and paragraphs
2- Semantic Markup
To provide extra informations such as where emphasisiid placed in a sentence.
Headings
HTML has six “levels” of headings:
Headings | Describtion —- | —— < h1 > | is used for main headings < h2 > | is used for subheadings ——
Paragraphs
TO create a pargraph, surround the words that make up the paragraph with an open and close tag.
< b >
By enclosing words in the tags and we can make characters appear bold
< i >
By enclosing words in the tags and we can make characters appear italic.
< sup >
The element is used to contain characters that should be superscript such as the suffixes of dates or mathematical concepts
< sub >
The element is used to contain characters that should be subscript. It is commonly used with foot notes or chemical formulas such as H20.
< br />
To start a sentence with a new line
< hr />
To create a break between to themes.
Visual editors
often resemble word processors. Although each editor will differ slightly, there are some features that are common to most editors that allow you to control the presentation of text.
Strong & Emphasis
they are being used to make the it bold or italic.
Quotations
< blockquote >
Is used for longer quotes that take up an entire paragraph
< q >
The element is used for shorter quotes that sit within a paragraph
Introduction to CSS

The key to understanding how CSS works is to imagine that there is aninvisiblebox around every HTML element.
CSS allows you to create rules that control the way that each individual box (andthe contents of that box) is presented
CSS Associates Style rules with HTML elements
CSS works by associating rules with HTML elements. These rules govern how the content of specified elements should be displayed. A CSS rule contains two parts: a selector and a declaration.
CSS Properties Affect How Elements Are Displayed.
CSS declarations sit inside curly brackets and each is made up of two parts: a property and a value, separated by a colon. You can specify several properties in one declaration, each separated byasemi-colon.
Using External CSS
CSS | Description —-| —- link | The element can be used in an HTML document to tell the browser where to find the CSS file used to style the page href | This specifies the path to the CSS file (which is often placed in a folder called css or styles) type | This attribute specifies the type of document being linked to. The value should be text/css rel|This specifies the relationship between the HTML page and the file it is linked to. The value should be stylesheet when linking to a CSS file. style | You can also include CSS rules within an HTML page by placing them inside a < style> element, which usually sits inside the <head> element of the page. ——————-
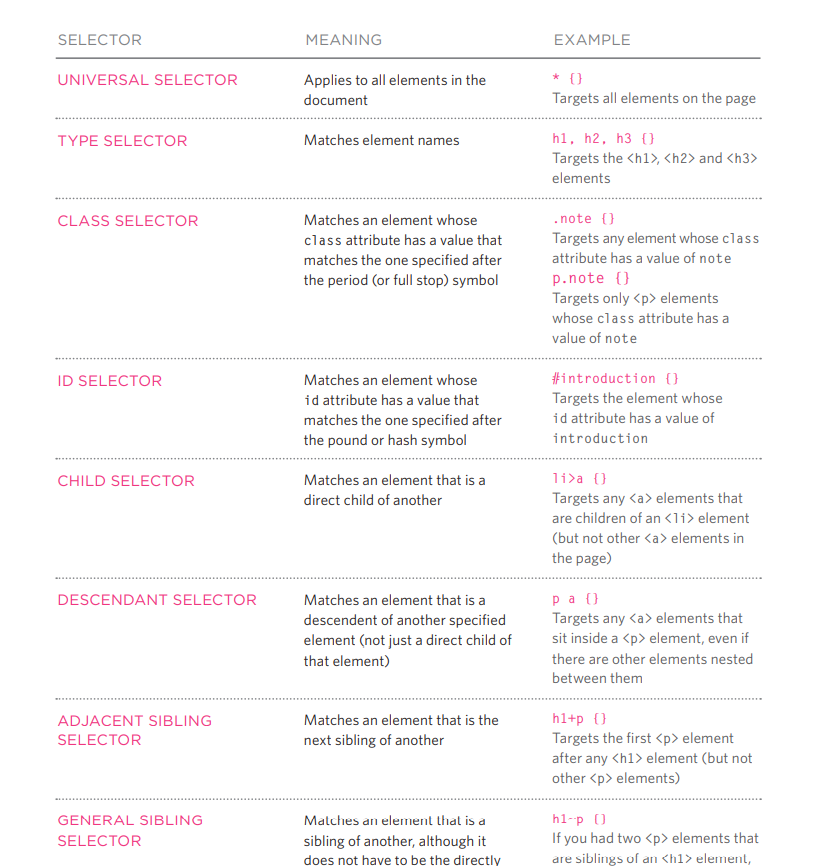
The Picture below show you the selectors amd its meaining
Basic JavaScript Instructions
What is script?
A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow one-by-one. Each individual instruction or step is known as astatement. Statements should end with a semicolon.
STATEMENTS ARE INSTRUCTIONS AND EACH ONE STARTS ON A NEW LINE
STATEMENTS ARE INSTRUCTIONS AND EACH ONE STARTS ON A NEW LINE
Comments
STATEMENTS ARE INSTRUCTIONS AND EACH ONE STARTS ON A NEW LINE
MULTI-LINE COMM ENTS
SINGLE-LINE COMMENTS
Variables
A script will have to temporarily store the bits of information it needs to do its job. It can store this data in variables.
To Declare a Variable, you need to write the following: Var variable name;
To assign a value into a variable, see the below:
quantity = 3;
DATA TYPES
Data Types | Description —|— NUMERIC | The numeric data type handles numbers. STRING | The strings data type consists of letters and other characters BOOLEAN |The strings data type consists of letters and other characters —–
There are six rules for naming a variable
Number | Description —- | —– 1|The strings data type consists of letters and other characters 2|The name can contain letters, numbers, dollar sign ($), or an underscore (_). 3|You cannot use keywords or reserved words. Keywords are special words that tell the interpreter to do something. 4|All variables are case sensitive, so score and Score would be different variable names 5|All variables are case sensitive,so score and Score would be different variable names 6|If your variable name is made up of more than one word, use a capital letter for the first letter of every word after the first word ————-
Arrays
what are the Arrays:
An array is a special type of variable. It doesn’t just store one value; it stores a list of values.
VALU ES IN ARRAYS
Values in an array are accessed as if they are in a numbered list. It is important to know that the numbering of this list starts at zero (not one).
Comparison Operators:
Evaluating Conditions
This command help us to evaluate a situation by comparing one value with a datatype to get the expected output. The result will be a boolean which is
* True
* False
Down below, we are going to see the symboles or a special characters that Java can read in order to interact with them:
Symbols | Meaning
- |- Equal to (==) | Comapring two values (Numbers, strings and booleans) to see if they are the same. Not equal to (!=) | to see if the two values are not the same (exact opposite of ==) Strict Equal to (===) |compares two values to check both the datatype and value are the same Stict not Equal (!==) | compares two values to check both the datatype and value are not the same Greater than > | to check if the number on the left is greater than of the right. Less than < | to check if the number on the left is less than of the right. Greater than or Equal >= | to check if the number on the left is greater than or equal of the right Less than or equal <= | to check if the number on the left is less than or equal of the right _________________________________
Logical Operators
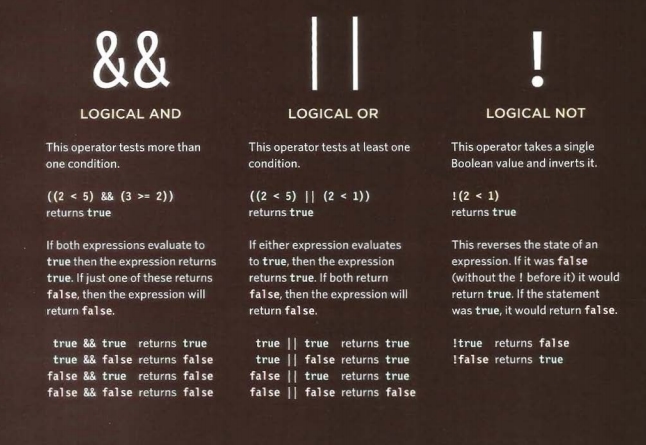
Comparison Operators often return single values of T or F, Which allow the users to compare the results more than one comparision Operator. Check the below image.

Now lets have a look of other logical Operators:
| Logical Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| && | its (AND) Logical where this Operator test more than one Condition.(see the image below table for more example). |
| (or) | tests at lesat one Condition (see the image below table for more example). |
| ! | takes a single boolean value and inverts it (see the image below table for more example). |